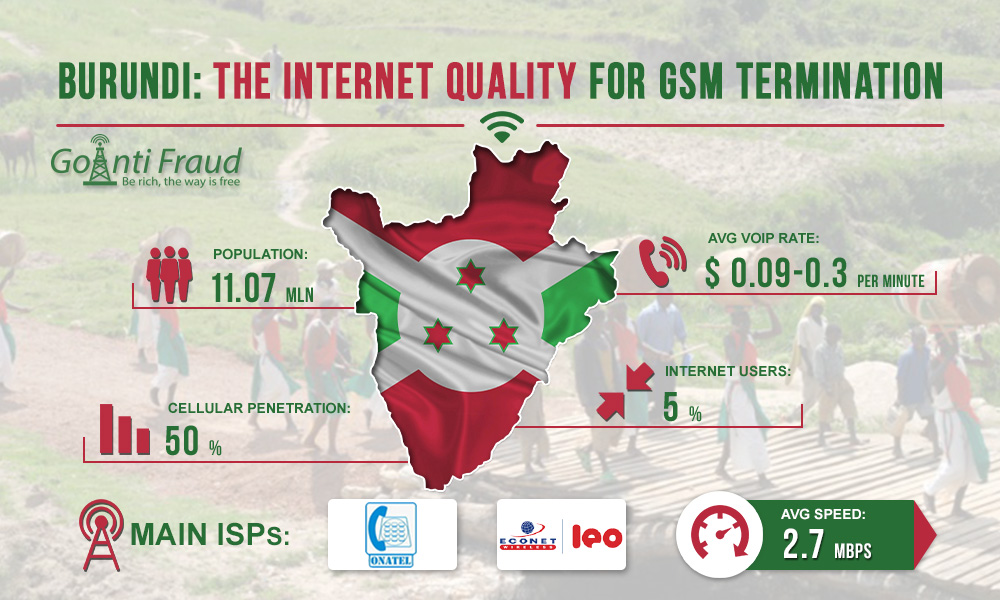
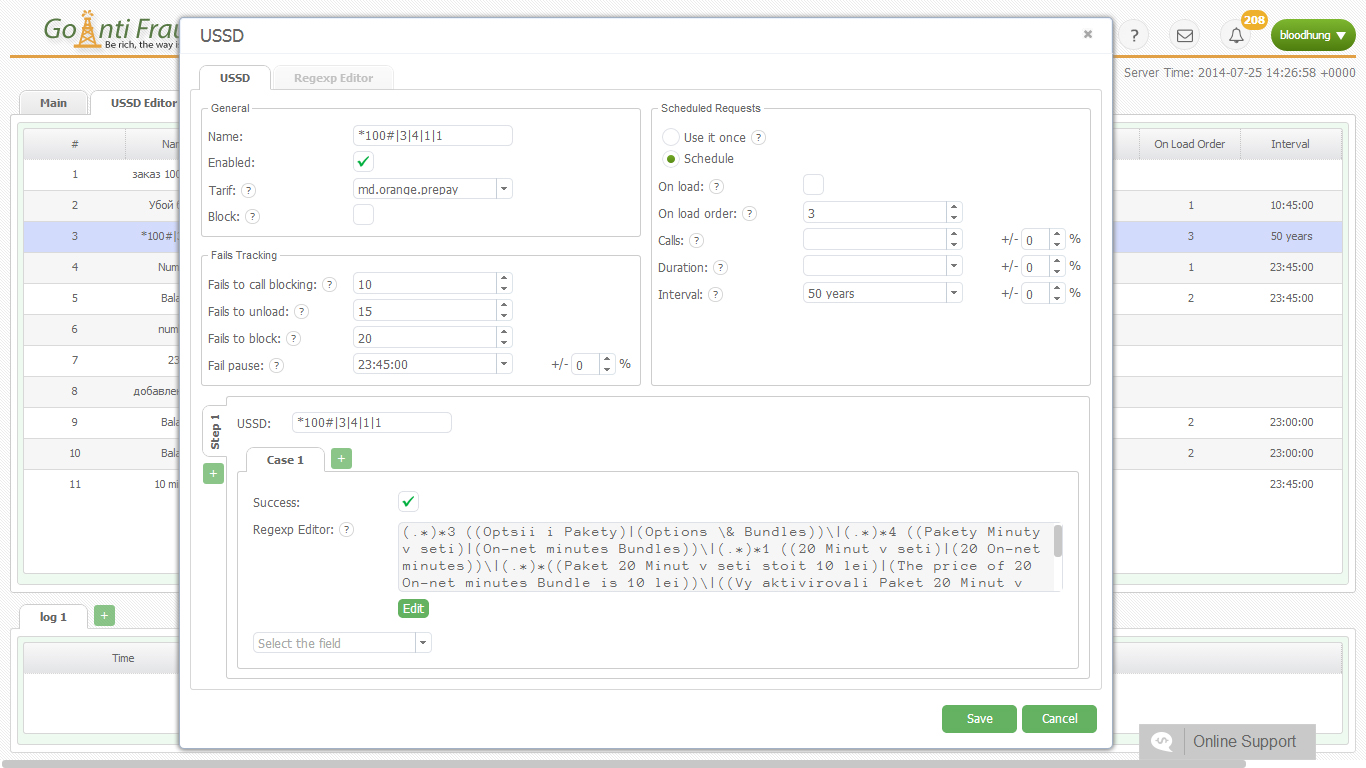
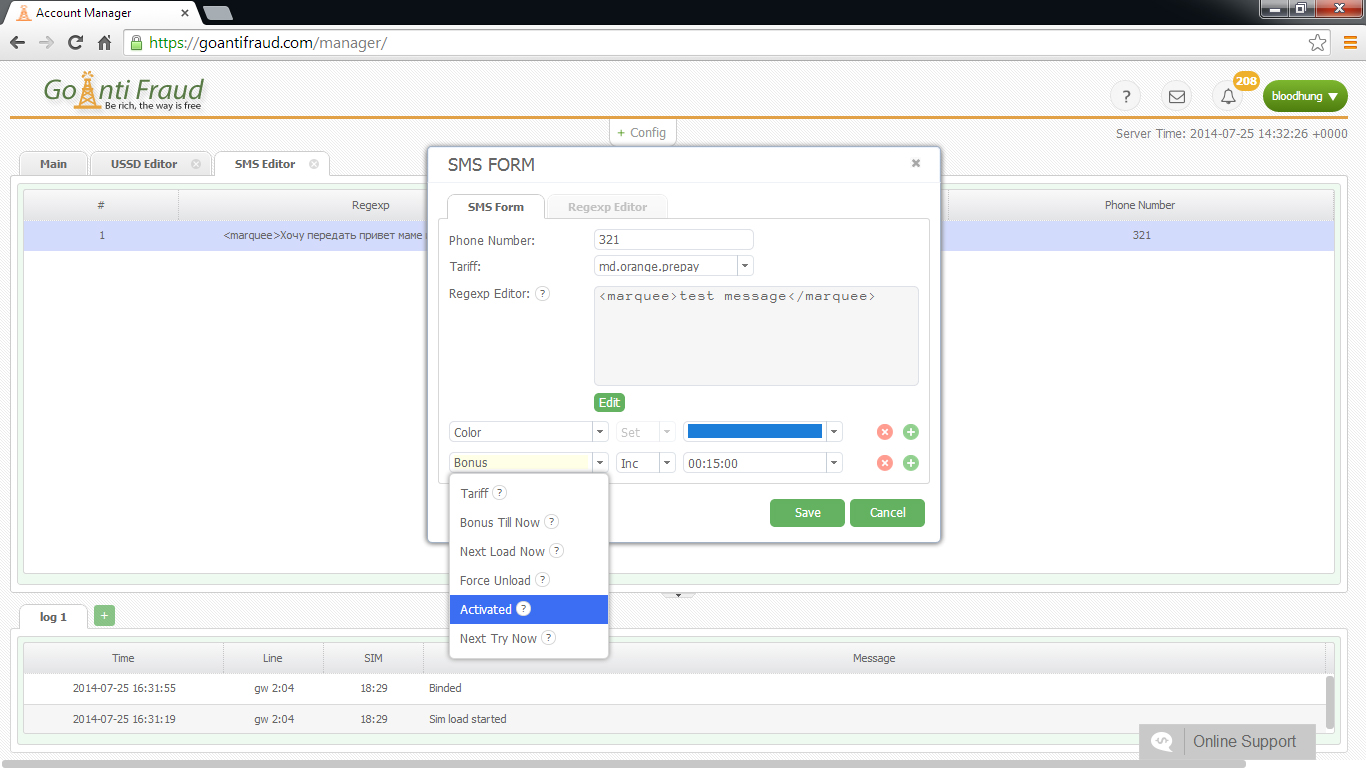
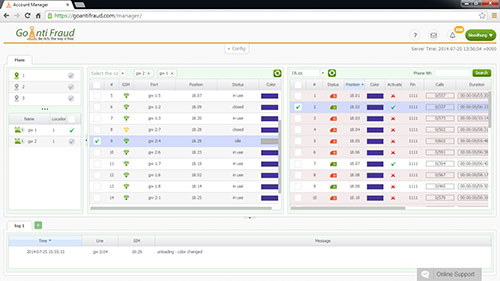
Burundi, like other African countries, can become a profitable route for terminating traffic. A fairly high rate in combination with the developed cellular market opens up broad prospects for the terminator. But what about the situation with the Internet? After all, you need a stable Internet connection with a speed of 42 Kbps per port to make sure that your GSM-gateways operate smoothly.
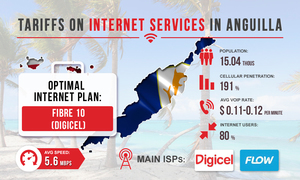
To date, the Internet sector in Burundi is poorly developed. The penetration rate of the Internet is as little as 5%, which is 0.57 million connections. This is due primarily to the poor state of the cellular communication infrastructure outside of large cities. Now 90% of connections to the Internet are made via the LTE network. The 3G and 4G Internet is not suitable for efficient termination.

Nevertheless, the government and foreign investors are making efforts to improve the situation. In 2014, Burundi began creating a national fiber-optic network with the connection to underwater cables of Kenya and Tanzania. In 2018, Burundi launched a project to improve broadband.
Thanks to the above measures, from 2014 to 2017, the network capacity in the country was significantly increased (by 5 times). This, in turn, reduced the tariffs on Internet services. The average Internet speed in Burundi is currently 2.7 Mbps. This speed is sufficient for normal operation of goip gsm gateway 3cx and converting VoIP calls to GSM. The main Internet providers in Burundi are Onatel and Econet Wireless. Basically, on the market, there are offers for connecting via ADSL technology.